Article written by Valentin Kuzmenko, Chief Commercial Officer/ VP of Sales
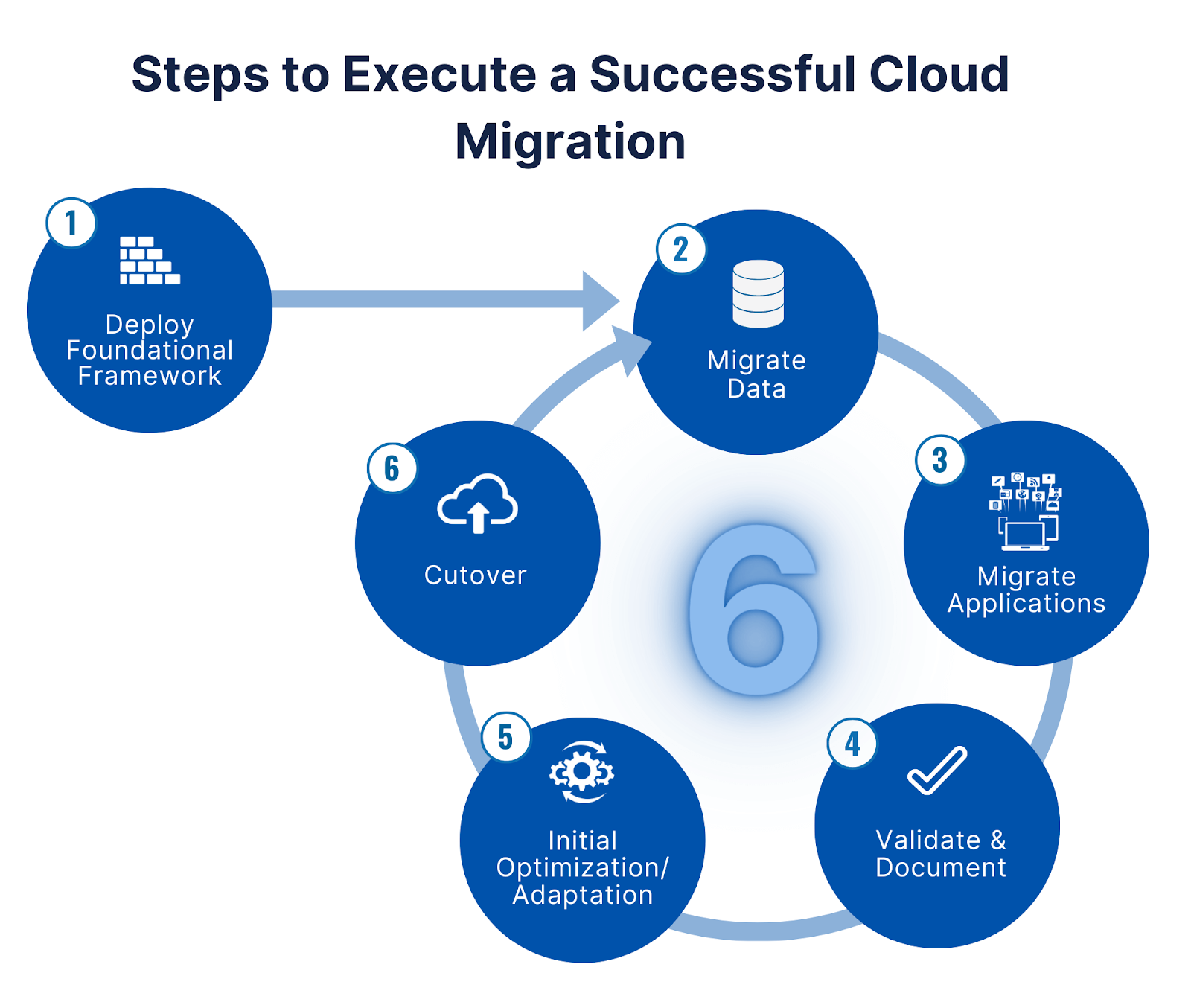
Cloud data migration is a process which allows businesses to stay competitive, and keep the in-house workflow cost-effective and beneficial for the organization. However, undertaking a successful migration requires meticulous assessment, planning and facing multiple cloud migration challenges.
In this article we are going to discuss the importance of conducting a comprehensive assessment of existing infrastructure as well as creating a detailed migration plan with all the possible obstacles on the way. By doing so, you can establish clear goals, establish realistic timelines, allocate necessary resources, and mitigate potential risks during the cloud data migration process.
Thorough Assessment and Planning
Comprehensive Assessment
a. Infrastructure evaluation: The limitations and potential problems of the cloud environment are identified by a thorough evaluation of the existing infrastructure. To guarantee a smooth transfer of data, analysis should be made of elements including network capacity, server capacities and security measures.
b. Application Analysis: It is useful for companies to establish dependencies, performance requirements and potential integration difficulties when they examine applications that are stored in the infrastructure. Priority for migration will be facilitated by classification of applications on the basis of criticality.
c. Data assessment: The technical challenges of cloud migration can be identified by companies when assessing the current data landscape. This assessment will help to identify redundant, obsolete or trivial data and thereby optimize storage costs in the cloud.
Detailed Migration Plan
a. Defining Clear Goals: Establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals is essential for the migration process. Goals may include improving data accessibility, or enabling remote data management.
b. Timelines and Milestones: Developing a timeline with clear milestones helps organizations manage expectations and ensure timely completion of the migration. Setting realistic milestones allows for necessary adjustments when unexpected cloud data migration challenges arise.
c. Resource Allocation: Assessing the required resources such as skilled personnel, tools, and budget will help organizations allocate necessary resources effectively.
d. Risk Identification and Mitigation: Identifying potential risks, such as security breaches, or service disruptions, is vital for developing contingency plans. Employing security measures and implementing data backup strategies minimizes the impact of unforeseen events, ensuring business continuity.
Prioritize Applications and Workloads
To ensure a smooth transition and minimize the cloud migration challenges, it is necessary to move all your applications and workloads into the cloud in a thoughtful and strategic way. Prioritizing applications according to their criticality, dependency and complexity is a key aspect of this process. Organizations can build trust and experience in advance of the migration of mission-critical applications by starting with low risk applications.
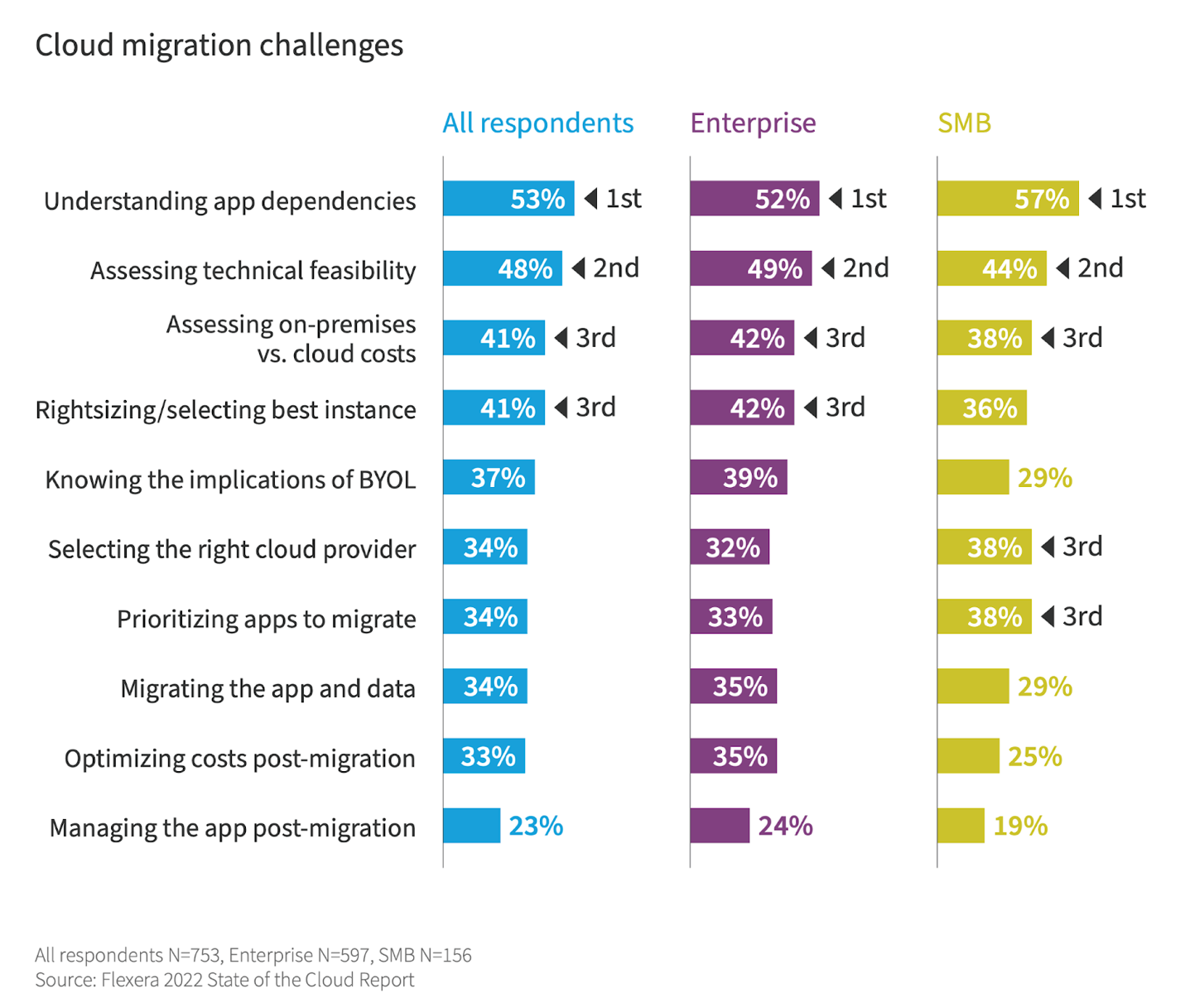
Understanding Application Criticality
Not all applications within an organization hold the same level of importance. Certain applications might be more critical to day-to-day operations or have higher dependencies on other systems. These applications often handle sensitive data, have strict performance requirements, or play a pivotal role in supporting critical business functions.
Mapping Application Dependencies
Dependency between applications and other systems such as databases, hybrid clouds, foreign services or APIs is frequently complex. Unforeseen complications and difficulties in continuity are likely to result from switching an application to the cloud not taking into account these dependencies. In order to address this challenge, it is necessary for the organizations to thoroughly map application dependencies and integrate them into their migration plan.
Assessing Application Complexity
Simplification of the migration process may be significantly affected by application complexity. Customizations, unique configurations that are not easily compatible with cloud environments, may exist in complex applications. The general migration process can be hampered, and the desired results lost if these applications are migrated in advance. You will gradually gain experience, improve migration strategies and understand how to deal with more complex scenarios through the introduction of simpler applications.
Building Confidence and Experience
Cloud migration can be intimidating, particularly for organizations with limited cloud adoption experience. By prioritizing the migration of low-risk applications initially, organizations can build confidence and learn from the process. These applications act as a testing ground for an organization’s cloud migration strategies, allowing them to identify and rectify any shortcomings or technical challenges. With each successful migration, the organization gains valuable expertise and can refine its processes, paving the way for a smoother transition when migrating mission-critical applications.
Choose the Right Cloud Environment
Data Security
One of the problems with cloud migration is data security. Businesses need to rely on cloud service providers for data protection in the context of Public Cloud Environments. The level of inherent risk associated with the storage of data in cloud computing remains high, even though certain information security service providers are implementing strong safety measures. Potential illegal access, data breaches and failure to comply with regulations have raised privacy and security concerns.
Compliance Requirements
Organizations in highly regulated industries, such as finance or healthcare, must adhere to stringent compliance requirements when storing and managing data. Public cloud environments might not fully meet these standards due to concerns regarding non-compliance with specific regulations or data residency requirements. In such cases, private cloud environments are often preferred as they offer greater control and customization options to meet the organization’s compliance needs.
Scalability
Scalability is a crucial consideration when selecting the right cloud environment. Public cloud environments offer virtually limitless capacity and allow organizations to seamlessly scale up or down as demand fluctuates. This elasticity enables businesses to handle sudden spikes in traffic or workload without significant upfront investments. It can be advantageous for organizations with dynamic or unpredictable requirements. On the other hand, private clouds provide a dedicated infrastructure that can handle predictable and consistent workloads effectively.
Ensure Data Security and Compliance
Maintaining compliance with relevant data protection regulations and industry standards is essential within challenges faced during cloud migration. Organizations must be aware of the legal and regulatory requirements that apply to their data, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. By ensuring compliance, organizations can avoid such cloud data migration challenges as hefty fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Conducting regular audits, implementing data classification processes, and monitoring data transfers and storage locations can help demonstrate compliance.
To overcome the challenges in cloud data migration, organizations should adopt a comprehensive approach that involves the collaboration of multiple stakeholders, including IT teams, data protection officers, and legal experts. Developing a well-defined data migration strategy that incorporates data security and compliance measures from the outset is essential. This strategy should include risk assessments, data classification, encryption protocols, access controls, and regular data integrity checks to ensure a smooth and secure migration process.
Testing and Validation
Rigorous Testing
To tackle the challenges of cloud migration, it is essential to undergo rigorous testing before executing a full-scale migration. By conducting comprehensive tests on a smaller scale or in controlled environments, potential issues can be identified and addressed early on. This approach allows for fine-tuning before the actual migration takes place, reducing the risk of downtime and ensuring a seamless transition.
Testing Application Functionality
Testing application functionality during cloud migration involves examining whether the applications behave as expected in the cloud environment. Factors to consider include the compatibility of the application with the cloud infrastructure, verifying the appropriate functioning of integrations with other applications, and ensuring adherence to service-level agreements (SLAs). Conducting tests in a staging environment allows for controlled simulation and verification of application behavior before deploying it in a live production environment.
Performance Testing
Speaking of more challenges faced during cloud migration, assessing the performance of applications in the cloud is critical to ensure optimal functionality and user experience. Performance testing involves testing the application under varying load conditions and stress scenarios to determine if it can handle the anticipated traffic volume. Cloud providers often offer tools and resources, often using automation testing tools as well, for load testing in staging environments, helping validate performance capabilities before the final migration. This ensures that applications can seamlessly scale, handle peak demands, and deliver consistent performance in the cloud.
Data Validation
Data integrity becomes one of the technical challenges in cloud migration as data migrates to the cloud. In a new environment, companies need to monitor accurate transfer, transformation and storage of data. The completeness, correctness and consistency of the migrated information shall be confirmed by a data validation test. This may involve comparing data on the source and destination systems, performing data reconciliations as well as checking that migration scripts and procedures are correct.
Skill Development and Training
The skill gap can have significant implications for cloud migration projects. Without proper training, teams may face difficulties understanding the complexities of cloud infrastructure, resulting in slower adoption rates, security vulnerabilities, and potential inefficiencies. Furthermore, limited knowledge of cloud platforms and tools may hinder organizations from effectively leveraging the full potential of cloud services, leading to missed opportunities for innovation and cost savings.
Benefits of Skill Development and Training
1. Smoother Migration:
Providing comprehensive training on cloud technologies helps employees gain a clear understanding of the migration process, enabling them to identify potential challenges and develop effective migration strategies. Training also familiarizes the workforce with cloud-native tools and methodologies, promoting efficient migration practices.
2. Improved Cloud Management:
Upskilling IT teams in cloud technologies equips them with the necessary knowledge to effectively manage the deployed cloud infrastructure. Well-trained employees can implement robust security measures, optimize resource allocation, and monitor performance, ensuring the long-term stability and reliability of cloud services.
3. Cost Optimization:
Cloud migration done without proper skill development may lead to suboptimal resource utilization, resulting in higher costs. Educating employees on cost management strategies specific to cloud platforms enables organizations to optimize resource consumption, improve efficiency, and drive cost savings.
4. Innovation and Agility:
A skilled workforce allows organizations to leverage advanced cloud services and emerging technologies. By training employees on cloud data migration challenges and deployment tools, businesses can unlock the potential of cloud-native solutions, enabling rapid development, testing, and scaling of applications. This fosters innovation, enhances agility, and ultimately improves the overall competitiveness of the organization.
Addressing the Skill Gap
To address the skill gap and ensure successful cloud migration, organizations should implement a comprehensive training and development strategy. This may include:
- Formal Training Programs: Offering structured training programs, both in-house and external, that cover various aspects of cloud technologies, including infrastructure, security, development methodologies, and management best practices.
- Certifications: Encouraging employees to pursue cloud-related certifications and providing assistance or incentives for their achievement. Certifications from reputable cloud service providers validate employees’ expertise and contribute to the confidence of the organization in its cloud migration goals.
- Hands-on Experience: Providing employees with opportunities to gain practical experience through real-world cloud projects and simulations. This hands-on approach enhances their understanding of cloud technologies, enabling effective problem-solving and troubleshooting.
- Continuous Learning: Encouraging a culture of continuous learning by providing access to up-to-date resources, online training platforms, and communities of practice where employees can share knowledge and best practices.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, cloud migration has become a crucial step for businesses to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and remain competitive. However, navigating the intricate process of cloud migration can pose significant challenges that may hinder organizations from achieving their desired outcomes. To avoid pitfalls and ensure a successful transition, many businesses turn to cloud migration consulting services for their expertise and guidance.